A Cautious, Upbeat Start to 2023
There was no shortage of gloom as the new year began. The Federal Reserve was signaling higher interest rates, and its aggressive campaign, started last year, to rein in inflation has been threatening to throw the economy into a profit-killing recession. While investor sentiment is far from euphoric right now, 2023 is off to a strong start. What’s behind the move?
Last year, the Fed hiked its key lending rate, the fed funds rate, by 75 basis points (bp, 1 bp – 0.01%) in four consecutive moves. Mix in a 50 bp increase in December and 25 bp increase back in March, and we experienced the most aggressive tightening cycle in over 40 years—1,000 bp in 6 months (St. Louis Federal Reserve) at the end of 1980. Ronald Reagan had not yet been inaugurated.
While the Federal Reserve is not yet signaling a halt to rate hikes and commentary suggests it could hold rates at a high plateau this year (what analysts have been calling ‘higher for longer’), the pace of rate increases is set to slow from last year’s nearly unprecedented level.
But are investors front-running the Fed? Or are they too optimistic about rates? Fed officials pushed back aggressively last year on a 2022 pivot. Today, investors believe we may see at least one rate cut by the end of the year. Previously, that had not been in the Fed’s game plan, but Fed Chief Powell seemed less wedded to pushing rates above 5% at the February 1 press conference. While Powell isn’t declaring victory on inflation and he isn’t ready to hint at a turnaround, he was more open to the recent moderation in inflation. The initial reaction was positive.
Looking ahead, a significant rise in the jobless rate would probably force the Fed to cut rates, but a drop in corporate profits could negate any benefits from falling rates. How the Fed responds will be heavily influenced by how the economic outlook unfolds.
An opaque crystal ball
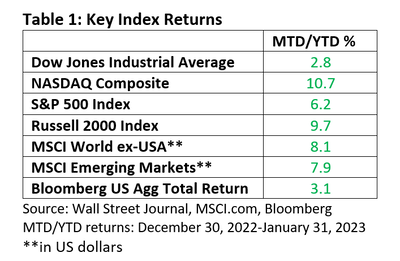
From 1970 through 2021, the January return on the S&P 500 Index exceeded 5% 10 times (St. Louis Federal Reserve data). Excluding reinvested dividends, the S&P 500 finished the year higher nine times. The 90% ‘win ratio’ beats the average since 1970 of 74%.
During the 10 years when January advanced by 5% or more, the S&P 500 averaged a return of 21.5%. Its best annual return was 31.6% in 1975, which followed the difficult 1973-74 bear market. Its only loss was 6.2% in 2018.
There are those who attempt to glean insights from expected market returns based on where we are in a political cycle. Such exercises are interesting, but let’s stress that each economic cycle has its own peculiarities that may override these barometers. We know that past performance is not a guarantee of future results. Ultimately, the economic fundamentals will play a big role as the year unfolds.
Last year, the Fed hiked its key lending rate, the fed funds rate, by 75 basis points (bp, 1 bp – 0.01%) in four consecutive moves. Mix in a 50 bp increase in December and 25 bp increase back in March, and we experienced the most aggressive tightening cycle in over 40 years—1,000 bp in 6 months (St. Louis Federal Reserve) at the end of 1980. Ronald Reagan had not yet been inaugurated.
While the Federal Reserve is not yet signaling a halt to rate hikes and commentary suggests it could hold rates at a high plateau this year (what analysts have been calling ‘higher for longer’), the pace of rate increases is set to slow from last year’s nearly unprecedented level.
But are investors front-running the Fed? Or are they too optimistic about rates? Fed officials pushed back aggressively last year on a 2022 pivot. Today, investors believe we may see at least one rate cut by the end of the year. Previously, that had not been in the Fed’s game plan, but Fed Chief Powell seemed less wedded to pushing rates above 5% at the February 1 press conference. While Powell isn’t declaring victory on inflation and he isn’t ready to hint at a turnaround, he was more open to the recent moderation in inflation. The initial reaction was positive.
Looking ahead, a significant rise in the jobless rate would probably force the Fed to cut rates, but a drop in corporate profits could negate any benefits from falling rates. How the Fed responds will be heavily influenced by how the economic outlook unfolds.
An opaque crystal ball
From 1970 through 2021, the January return on the S&P 500 Index exceeded 5% 10 times (St. Louis Federal Reserve data). Excluding reinvested dividends, the S&P 500 finished the year higher nine times. The 90% ‘win ratio’ beats the average since 1970 of 74%.
During the 10 years when January advanced by 5% or more, the S&P 500 averaged a return of 21.5%. Its best annual return was 31.6% in 1975, which followed the difficult 1973-74 bear market. Its only loss was 6.2% in 2018.
There are those who attempt to glean insights from expected market returns based on where we are in a political cycle. Such exercises are interesting, but let’s stress that each economic cycle has its own peculiarities that may override these barometers. We know that past performance is not a guarantee of future results. Ultimately, the economic fundamentals will play a big role as the year unfolds.